
Maple provides a state-of-the-art environment for algebraic computations in Physics, with emphasis on ensuring that the computational experience is as natural as possible. The theme of the Physics project for Maple 2020 has been the consolidation of the functionality introduced in previous releases, together with significant enhancements to further strengthen the functionality especially in:
Overall, the enhancements throughout the entire package further extend the range of Physics-related algebraic computations that can be done naturally in a worksheet. The presentation below illustrates both the novelties and the kind of mathematical formulations that can now be performed.
As part of its commitment to providing the best possible environment for algebraic computations in Physics, Maplesoft launched a Maple Physics: Research and Development website in 2014, which enabled users to download research versions, ask questions, and provide feedback. The results from this accelerated exchange with people around the world have been incorporated into the Physics package in Maple 2020.
Feynman Diagrams - the scattering matrix in coordinates and momentum representation
![]()
![]()
![]()
Examples
For illustration purposes set three coordinate systems, and set ![]() to represent a quantum operator
to represent a quantum operator
| > |
| > |
| (1) |
Let ![]() be the interaction Lagrangian
be the interaction Lagrangian
| > |
| (2) |
The expansion of ![]() in coordinates representation, computed by default up to order = 3 (you can change that using the option order = n), by definition containing all possible configurations of external legs, displaying the related Feynman Diagrams, is given by
in coordinates representation, computed by default up to order = 3 (you can change that using the option order = n), by definition containing all possible configurations of external legs, displaying the related Feynman Diagrams, is given by
| > |
|
||||||||||||
| (3) |
The expansion of ![]() in coordinates representation to a specific order shows in a compact way the topology of the underlying Feynman diagrams. Each integral is represented with a new command, FeynmanIntegral, that works both in coordinates and momentum representation. To each term of the integrands corresponds a diagram, and the correspondence is always clear from the symmetry factors and normal products shown.
in coordinates representation to a specific order shows in a compact way the topology of the underlying Feynman diagrams. Each integral is represented with a new command, FeynmanIntegral, that works both in coordinates and momentum representation. To each term of the integrands corresponds a diagram, and the correspondence is always clear from the symmetry factors and normal products shown.
In a typical situation, one wants to compute a specific term, or scattering process, instead of the S matrix up to some order with all possible configurations of external legs. For example, to compute only the terms of this result above that correspond to diagrams with 1 loop use numberofloops = 1 (for tree-level, use numberofloops = 0)
| > |
|
||
| (4) |
In the result above there are two terms, with 4 and 6 external legs respectively.
A scattering process with matrix element ![]() in momentum representation, corresponding to the term with 4 external legs (symmetry factor = 72), could be any process where the total number of incoming + outgoing particles is equal to 4. For example, one with 2 incoming and 2 outgoing particles. The transition probability for that process is given by
in momentum representation, corresponding to the term with 4 external legs (symmetry factor = 72), could be any process where the total number of incoming + outgoing particles is equal to 4. For example, one with 2 incoming and 2 outgoing particles. The transition probability for that process is given by
| > |
|
|
   |
(5) |
When computing in momentum representation, only the topology of the corresponding Feynman diagrams is shown (i.e. the diagrams associated to the corresponding Feynman integral in coordinates representation).
The transition matrix element ![]() is related to the transition probability density
is related to the transition probability density ![]() (formula (13) of sec. 21.1 of ref.[1]) by
(formula (13) of sec. 21.1 of ref.[1]) by
![dw = `*`(`^`(`+`(`*`(2, `*`(Pi))), `+`(`*`(3, `*`(s)), `-`(4))), `*`(n__1, `*`(`...`, `*`(n__s, `*`(`^`(abs(F(p[i], p[f])), 2), `*`(delta(`+`(sum(p[i], i = 1 .. s), `-`(sum(p[f], f = 1 .. r)))), `*`(`...](physics/Physics_61.gif)
where ![]() represent the particle densities of each of the s particles in the initial state
represent the particle densities of each of the s particles in the initial state ![]() , the
, the ![]() (Dirac) is the expected singular factor due to the conservation of the energy-momentum and the amplitude
(Dirac) is the expected singular factor due to the conservation of the energy-momentum and the amplitude ![]() is related to
is related to ![]() via
via

To directly get the probability density ![]() instead of
instead of![]() use the option output = probabilitydensity
use the option output = probabilitydensity
| > |
 |
(6) |
In practice, the most common computations involve processes with 2 or 4 external legs. To restrict the expansion of the scattering matrix in coordinates representation to that kind of processes use the numberofexternallegs option. For example, the following computes the expansion of ![]() up to order = 3, restricting the outcome to the terms corresponding to diagrams with only 2 external legs
up to order = 3, restricting the outcome to the terms corresponding to diagrams with only 2 external legs
| > |
|
|||
| (7) |
This result shows two Feynman integrals, with respectively 2 and 3 loops, the second integral with two terms. The transition probability density in momentum representation for the process ![]() corresponding to the first integral (1 term with symmetry factor = 96) is then
corresponding to the first integral (1 term with symmetry factor = 96) is then
| > |
|
|
 |
(8) |
In the above, for readability, the contracted spacetime indices in the square of momenta entering the amplitude F (as denominators of propagators) are implicit. To make those indices explicit, use the option putindicesinsquareofmomentum
| > |
  |
(9) |
This computation can also be performed to higher orders. For example, with 3 loops, in coordinates and momentum representations, corresponding to the other two terms and diagrams in (7)
| > |
| (10) |
| > |
 |
(11) |
Consider the interaction Lagrangian of Quantum Electrodynamics (QED). To formulate the problem start defining the vector field ![]() .
.
| > |
| (12) |
Set lowercase Latin letters from i to s to represent spinor indices (you can change this setting according to your preference using Setup), also the (anticommutative) spinor field will be represented below by ![]() , so set
, so set ![]() as an anticommutativeprefix, and set
as an anticommutativeprefix, and set ![]() and
and ![]() as quantum operators
as quantum operators
| > |
| (13) |
The matrix indices of the Dirac matrices are written explicitly and use conjugate to represent the Dirac conjugate ![]()
| > |
| (14) |
Compute ![]() , only the terms with 4 external legs, and display the diagrams: they have no loops
, only the terms with 4 external legs, and display the diagrams: they have no loops
| > |
|
||
| (15) |
The same computation but with only 2 external legs results in the diagrams with 1 loop that correspond to the self-energy of the electron and the photon (page 218 of ref.[1])
| > |
|
||
| (16) |
where the diagram with two spinor legs is the electron self-energy.
To restrict the output furthermore, for example getting only the self-energy of the photon, you can specify the normal products you want:
| > |
 |
(17) |
The corresponding S-matrix elements in momentum representation
| > |
|
|
  |
(18) |
where ![]() is the corresponding polarization vector.
is the corresponding polarization vector.
The self-energy of the electron:
| > |
 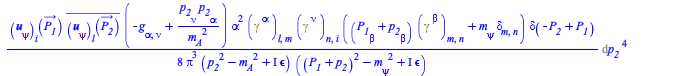 |
(19) |
In this result we see the ![]() spinor (see ref.[2]), and the propagator of the field
spinor (see ref.[2]), and the propagator of the field ![]() with a mass
with a mass ![]() . To indicate that this field is massless use
. To indicate that this field is massless use
| > |
| (20) |
Now the propagator for ![]() is the one of a massless vector field:
is the one of a massless vector field:
| > |
 |
(21) |
When working with non-Abelian gauge fields, the interaction Lagrangian involves derivatives.
FeynmanDiagrams
can handle that kind of interaction in momentum representation. Consider for instance a Yang-Mills theory with a massless field ![]() where a is a SU2 index (see eq.(12) of sec. 19.4 of ref.[1]). The interaction Lagrangian can be entered as follows
where a is a SU2 index (see eq.(12) of sec. 19.4 of ref.[1]). The interaction Lagrangian can be entered as follows
| > |
| (22) |
| > |
| > |
| (23) |
| > |
| (24) |
The transition probability density at tree-level for a process with two incoming and two outgoing B particles is given by
| > |
|
|
         |
(25) |
| > |
| (26) |
This process can be computed with 1 or more loops, in which case the number of terms increases significantly. As another non-Abelian model, consider the interaction Lagrangian of the electro-weak part of the Standard Model
| > |
| (27) |
| > |
| (28) |
| > |
| (29) |
| > |
| (30) |
| > |
| (31) |
| > |
| (32) |
| > |
| (33) |
This interaction Lagrangian contains six different terms. The S-matrix element for the tree-level process with two incoming and two outgoing W particles is shown in the help page for FeynmanDiagrams. There, due to the use of size simplification and the option factortreelevel, the result is a product of 10 factors each of which is nested several times, totaling a computational length of 23,750. Expanding that product the computational length is 325,761 and the number of terms is 480, giving an idea of how fast the size of the S-matrix elements grow with the number of terms in the interaction Lagrangian.
[1] Bogoliubov, N.N., and Shirkov, D.V. Quantum Fields. Benjamin Cummings, 1982.
[2] Weinberg, S., The Quantum Theory Of Fields. Cambridge University Press, 2005.
The slicing and spatial gauge conditions of the 3+1 decomposition of spacetime
A key feature of the 3+1 decomposition of Einstein's equations is the freedom in the choice of coordinates and foliation (3D hypersurface), represented by the freedom of choice for the Lapse and Shift functions, frequently referred as the slicing and spatial gauge conditions respectively, entering the 3+1 equations. Only a few of the possible choices are actually useful for the purpose of numerical simulations of the solutions of the 3+1 equations. Depending on the problem, finding suitable conditions is still a research topic.
Some Lapse and Shift conditions, however, are well understood and useful in different contexts. Those conditions, entailing non-trivial algebraic relationships, are difficult to remember or to input for further manipulations, and crucial in that they determine the actual form of the 3+1 equations.
In connection, for Maple 2020 the Physics:-ThreePlusOne package includes a new command LapseAndShiftConditions, that return the equations of the most common slicing and spatial gauge conditions, optionally attempting to solve them for the Lapse and Shift.
| > |
| (34) |
To see the conditions implemented in this first version of LapseAndShiftConditions, you can enter the command with no arguments
| > |
| (35) |
To see the condition equations behind these keywords in this first version of LapseAndShiftConditions, use
| > |
 = `+`(`-`(`*`(2, `*`(%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace])))), `+`(%d_[0](Lapse), `-`(`*`(Shift[`~j`], `*`(%d_[j](Lapse))))) = `+`(`...](physics/Physics_211.gif) |
|
 = `+`(`-`(`*`(`^`(Lapse, 2), `*`(%f(Lapse), `*`(%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace]))))), Shift[`~i`] = 0], subtype = Vector[column]);](physics/Physics_213.gif) |
|
![geodesicslicing = rtable(1 .. 2, [Lapse = 1, Shift[`~i`] = 0], subtype = Vector[column]);](physics/Physics_215.gif) |
|
, `-`(`*`(Shift[`~j`], `*`(%d_[j](Lapse))))) = `+`(`-`(`*`(`^`(Lapse, 2), `*`(%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace])))), `+`(%d_[0](Shift[`~i`]), `-`(`*`(Sh...](physics/Physics_217.gif) |
|
 = `+`(`-`(`*`(`^`(Lapse, 2), `*`(%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace])))), Lapse = `*`(%C(x, y, z, t), `*`(sqrt(%gamma3_[determinant]))), Shift[`~i`] = 0], subtyp...](physics/Physics_219.gif) |
|
 = `*`(%c, `*`(%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace])), %d_[0](Lapse) = `+`(`-`(`*`(%epsilon, `*`(`+`(%d_[0](%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace]), `*`(%c, `*`(%...](physics/Physics_221.gif) |
|
![maximalslicing = rtable(1 .. 2, [%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace] = 0, %d_[0](%ExtrinsicCurvature[trace]) = 0, D_[`~mu`](D_[mu](Lapse)) = `*`(Lapse, `*`(`+`(`*`(%ExtrinsicCurvature[mu, nu], `*`(%ExtrinsicCu...](physics/Physics_223.gif) |
|
 |
(36) |
In the compact equations above, these condition equations for the Lapse and Shift include other tensors of the ThreePlusOne package, expressed in terms of their inert forms (displayed in grey) to allow for further manipulations. To retrieve these equations using these keywords, you can pass any them complete or, if you don't remember the exact spelling, just a portion of them suffices. For example,
| > |
 |
(37) |
These conditions form a system of equations for the Lapse and Shift that, depending on the 4D metric set, may be solvable in exact form. For example, the metric set at this point is the default metric when Physics loads
| > |
 |
(38) |
and for this metric two exact solutions for the Lapse and Shift are
| > |
| (39) |
where the RootOf in the second set implies on
| > |
| (40) |
These results can be obtained step by step manipulating the equations (37) themselves, in which case it is more convenient to have them evaluated first. For that purpose use the option evaluate, and set the Lapse and Shift to arbitrary so that the ExtrinsicCurvature (or any other tensor of ThreePlusOne) is not prematurely evaluated in terms of the Minkowski metric (38) (comments about this further below)
| > |
| (41) |
Now, instead of ![]() = 0 we have the trace expressed in terms of arbitrary Lapse and Shift
= 0 we have the trace expressed in terms of arbitrary Lapse and Shift
| > |
![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`-`(`/`(`*`(`+`(`*`(Physics:-ThreePlusOne:-Shift[`~1`], `*`(diff(Physics:-ThreePlusOne:-Lapse, x), `*`(`^`(Physics:-ThreePlusOne:-Lapse, 2)))), `*`(Physics:-ThreePlusOne:...](physics/Physics_244.gif) |
(42) |
and so, recomputing the equations ![]() using the evaluate option, we have
using the evaluate option, we have
| > |
 |
(43) |
Substitute the equations for the Shift, ![]() , into the equations for the Lapse
, into the equations for the Lapse ![]()
| > |
| (44) |
| > |
| (45) |
It is now possible to see that this system has two solutions: either ![]() (the second solution in (39), resulting in (40)) or the Lapse
(the second solution in (39), resulting in (40)) or the Lapse ![]() does not depend on t (the first solution in (39)).
does not depend on t (the first solution in (39)).
To understand the need, in (41), to set the lapseandshift to arbitrary, check what happens with the default value ![]()
| > |
| (46) |
Trying to reproduce the computation above, the first step works
| > |
 |
(47) |
but because of ![]() , in the next step the derivative of the Lapse is computed rewriting the Lapse in terms of the Minkowski metric (38), for which the Lapse is actually equal to 1
, in the next step the derivative of the Lapse is computed rewriting the Lapse in terms of the Minkowski metric (38), for which the Lapse is actually equal to 1
| > |
, `*`(Physics:-D_[`~mu`](t, [X]))))))))], [Physics:-ThreePlusOne:-Lapse = `/`(1, `*`(sqrt(`+...](physics/Physics_272.gif) |
(48) |
| > |
| (49) |
and so, the step that results in (45), here results in nothing
| > |
| (50) |
The key observation is understanding what is defined (expressed) in terms of what. Given a 4D metric ![]() , when
, when ![]() the Lapse and Shift are defined in terms of the components
the Lapse and Shift are defined in terms of the components ![]() . That is why in (49) we have
. That is why in (49) we have ![]() . On the other hand, when
. On the other hand, when ![]() the Lapse and Shift are not expressed in terms of the metric, they remain arbitrary, allowing for solving the condition equations in order to then express the components
the Lapse and Shift are not expressed in terms of the metric, they remain arbitrary, allowing for solving the condition equations in order to then express the components ![]() in terms of the Lapse and Shift.
in terms of the Lapse and Shift.
An example where the conditions can be solved exactly and the spacetime is curved: set the Schwarzschild metric in spherical coordinates
| > |
 |
(51) |
Consider the harmonicslicing conditions
| > |
 |
(52) |
Note that in spite of having ![]() , in the internal intermediate computations of LapseAndShiftConditions
, in the internal intermediate computations of LapseAndShiftConditions ![]() is used, so the problem can be formulated and tackled in the right way, resulting in the right conditions equations when using the option evaluate, allowing to compute a solution
is used, so the problem can be formulated and tackled in the right way, resulting in the right conditions equations when using the option evaluate, allowing to compute a solution
| > |
   |
(53) |
| > |
| (54) |
The new explore option of TensorArray
TensorArray is one of the most frequently used commands to see the components of tensors or tensorial expressions. The functionality is extremely useful and simple when the tensorial expression has at most 2 free indices, but things are not so simple when that number is 3 or larger. For this purpose, in Maple 2020 TensorArray has a new explore option, that allows for a quick and simple exploration of the components of tensorial expressions with an arbitrarily large number of indices.
| > |
Although the new explore option is useful in general, the typical situation is that of tensorial expressions in curved spaces, so for illustration set the metric to something non-flat
| > |
| > |
| (55) |
Define now two tensors
| > |
 |
(56) |
| > | ![B[mu, nu] = Matrix(4, {(1, 1) = `/`(`*`(sqrt(`+`(`-`(`*`(k, `*`(`^`(r, 2)))), 1))), `*`(a(t))), (2, 2) = `/`(1, `*`(a(t), `*`(r))), (3, 3) = `/`(1, `*`(a(t), `*`(r, `*`(sin(theta))))), (4, 4) = 1});](physics/Physics_315.gif) |
 |
(57) |
| > |
| (58) |
Consider now the tensorial expression
| > |
| (59) |
This expression has 3 free indices
| > |
| (60) |
Passing this expression to TensorArray does not allow for a simple visualization because it only shows a slice of the 3-dimensional array of components
| > |
 |
(61) |
Moreover, there is the issue about which indices are being shown, in what order, and what is the value of the index not being shown. The interpretation of the matrix of components above is thus not straightforward.
The new explore option compacts all the interactive information above ((59), (60), (61)) in one go and resolves the interpretation issues on the indices shown and not shown:
| > |
| (62) |
|
|
In this output we see:
When the number of free indices is larger, being able to explore is even more significant. For example, for the product of the three non-contracted Ricci tensors ![]()
| > |
| (63) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
The ability to specify the ordering of the free indices is relevant in general, but more specifically in the case of tensorial expressions like this one: although you can specify which indices are assuming values (and in that way chose their relative ordering) the information on the ordering of the indices of the 2x2 slice, being displayed in the title, may or may not be the one you want, and can only be adjusted with the option freeindices = [...]: the 2x2 slice always corresponds to the two indices of the ordering list that remain after you remove all of Index 1 to Index 4 (by default, they are the last two). So to change that use the option freeindices of TensorArray.
Differentiating the spacetime metric, the tetrad, and their determinants, with respect to each other
Maple 2020's Physics comes with several improvements in the underlying routines for differentiating tensorial expressions with respect to the spacetime metric, a relevant operation when computing field equations. The improvements also include differentiation of the tetrad ![]() or with respect to it, of the determinant of the metric and the tetrad, and related manipulations with inert versions of these tensors.
or with respect to it, of the determinant of the metric and the tetrad, and related manipulations with inert versions of these tensors.
In what follows, the new differentiation formulas implemented in Maple 2020 are introduced, then the new manipulation capabilities are used to demonstrate them, finally these formulas are used in two examples: verifying a scalar identity and computing the energy-momentum tensor for the Proca Lagrangian density.
Differentiating the spacetime metric![]() with respect to itself
with respect to itself
For illustration purposes set up the general case, that of an arbitrary metric
| > |
 |
(64) |
As it happens with any tensor, the derivative of the metric with respect to itself has an obvious result when the indices of the derivand and the differentiation metric have the same character (covariant or contravariant):
| > |
| (65) |
If the character of the derivand and the differentiation variable are the opposite, the result is less obvious:
| > |
 |
(66) |
Demonstration
To demonstrate it, consider the identity
| > |
| (67) |
| > |
| (68) |
Differentiate this identity with respect to ![]()
| > |
 |
(69) |
Among the new manipulations possible in Maple 2020, you can expand inert derivatives without having them computed, an operation frequently required when deriving formulas
| > |
 |
(70) |
The element we are interested in is a factor of the first term; isolate it
| > |
 |
(71) |
To remove ![]() , multiply both sides of the equation by
, multiply both sides of the equation by ![]() , and use the dot operator `.` in order to multiply and simplify the indices in one go
, and use the dot operator `.` in order to multiply and simplify the indices in one go
| > |
 |
(72) |
On the right-hand side, the first derivative, ![%diff(g_[mu, `~xi`], g_[`~alpha`, `~beta`]);](physics/Physics_401.gif) , is equal to zero since the derivand is a constant. The second derivative,
, is equal to zero since the derivand is a constant. The second derivative, ![%diff(g_[`~nu`, `~xi`], g_[`~alpha`, `~beta`]);](physics/Physics_402.gif) is the easy case (65), so we have
is the easy case (65), so we have
| > |
 |
(73) |
Simplifying the contracted indices we arrive at the desired result (66)
| > |
 |
(74) |
Differentiating the tetrad ![]() with respect to itself
with respect to itself
First the easy case, where the covariant and contravariant characters of the tensorial derivand and differentiation variable are the same
| > |
 |
(75) |
from where
| > |
| (76) |
Differentiating with respect to the inverse tetrad:
| > |
 |
(77) |
Demonstration
Consider the identity satisfied by the tetrad by definition
| > |
| (78) |
| > |
| (79) |
Differentiate this identity with respect to ![]()
| > |
 |
(80) |
| > |
 |
(81) |
The element we are interested in is a factor of the first term; isolate it
| > |
 |
(82) |
To remove ![]() , multiply both sides of the equation by
, multiply both sides of the equation by ![]() , and use the dot operator `.` in order to multiply and simplify the indices in one go
, and use the dot operator `.` in order to multiply and simplify the indices in one go
| > |
 |
(83) |
On the right-hand side, the first derivative is equal to zero since the derivand is a constant. The second derivative is the easy case of differentiation of a tensor with respect to itself and same character of its indices, so we have
| > |
 |
(84) |
The desired result, (77), is obtained simplifying the contracted indices
| > |
 |
(85) |
Differentiating the spacetime metric ![]() with respect to the tetrad
with respect to the tetrad ![]()
| > |
| (86) |
Demonstration
Depart from the definition ![]() with both spacetime indices covariant
with both spacetime indices covariant
| > |
| (87) |
| > |
| (88) |
| > |
| (89) |
Results for the two derivatives on the right-hand side were already derived in the previous sections, so
| > |
| (90) |
| > |
| (91) |
Analogously,
| > |
 |
(92) |
Differentiating with respect to the inverse tetrad changes a sign
| > |
 |
(93) |
This result can be demostrated as done above for ![]() , changing
, changing ![]() by
by ![]()
Example: the vanishing of certain combinations of derivatives of a scalar
For background on this example, see the Appendix in: J. Struckmeier, D. Vasak1, and J. Kirsch1, "Generic Theory of Geometrodynamics from Noether's theorem for the Diff(M) symmetry group" . Define two arbitrary 2-rank tensors and use them to define a scalar S
| > |
| (94) |
| > |
| (95) |
The following combination of derivatives is equal to 0; use delay evaluation quotes to see the expression echoed in the output, more readable with typesetting
| > |
 |
(96) |
Unleash the delay evaluation quotes ''
| > |
| (97) |
Compute a value for (i.e., activate) the inert derivatives
| > |
| (98) |
| > |
| (99) |
An alternative formulation expressing the spacetime metric entering S in terms of tetrads
| > |
| (100) |
| > |
| (101) |
| > |
| (102) |
| > |
| (103) |
Differentiating the determinant of the metric with respect to the metric
The following results are necessary when one works with relative tensors of some weight and in particular with tensor densities. This derivative is also relevant in general relativity when computing field equations.
Given any 2-rank tensor (representable by a 2x2 matrix), the design in the Physics package is that its determinant is computed when you index the tensor with the keyword determinant. For example, for the arbitrary metric g_ set at this point,
| > |
| (104) |
Depending on the formulation, however, to perform algebraic manipulations what is required is a representation of the determinant, not its computed value. For that purpose use the inert form
| > |
| (105) |
that you can activate when desired using value .
| > |
| (106) |
From the general rule for the derivative of the determinant of a matrix M with respect to one of its components, ![]() , taking
, taking ![]() and
and ![]() , the derivative of the determinant of the metric is proportional to itself, and this rule is understood in Maple 2020 when you use the inert representation
, the derivative of the determinant of the metric is proportional to itself, and this rule is understood in Maple 2020 when you use the inert representation ![]()
| > |
| (107) |
The derivative with respect to the contravariant components follows from the above by taking into account that ![]() , hence
, hence ![]() so that
so that
| > |
 |
(108) |
Analogously, the derivative of the determinant of the tetrad with respect to the tetrad is computed using the inert form %e_ to represent the determinant
| > |
| (109) |
| > |
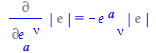 |
(110) |
| > |
 |
(111) |
Consequently,
| > |
 |
(112) |
Demonstration
Demonstrations for all of (109), (110) or (111) can be done in one and the same way: depart from the identity (87) written in terms of the all covariant tetrad
![]()
Taking the determinant of each side of this equation, defining ![]() and recalling that the determinant of a product is equal to the product of the determinants,
and recalling that the determinant of a product is equal to the product of the determinants,
![]()
In the case of an orthonormal tetrad, ![]() , while for a null tetrad,
, while for a null tetrad, ![]() . So in both cases we can rewrite this expression as
. So in both cases we can rewrite this expression as
![]()
From where, choosing the principal branch of the square root,
| > |
| (113) |
Note: in the case of a null tetrad, ![]() , and so
, and so ![]() . On the other hand, in the (default) case of an orthonormal tetrad,
. On the other hand, in the (default) case of an orthonormal tetrad, ![]() is a Minkowski metric with
is a Minkowski metric with ![]() , and so
, and so ![]()
Differentiating ![]() with respect to the tetrad
with respect to the tetrad
| > |
| (114) |
| > |
| (115) |
Using the chain rule and the differentiation rules for ![]() derived in the previous sections we obtain
derived in the previous sections we obtain
| > |
 |
(116) |
which in view of (113) can be written as ![]()
For (110),
| > |
 |
(117) |
| > |
 |
(118) |
Taking into account (113) this result can be written as ![%diff(%e_[determinant], e_[a, `~nu`]) = `+`(`-`(`*`(`𝔢`[`~a`, nu], `*`(%e_[determinant]))));](physics/Physics_547.gif)
Example: the components of the Energy-Momentum tensor for the Proca Lagrangian density
To express the Proca Lagrangian density, define the tensors entering the formulation
| > |
| (119) |
| > |
| (120) |
The Lagrangian:
| > |
| (121) |
By definition, the contravariant components of the energy momentum tensor are given by
| > |
 |
(122) |
Instead of using value
on the whole expression, which would result in the computation of ![]() , selectively activate %diff and %L
, selectively activate %diff and %L
| > |
![T[`~nu`, `~mu`] = `+`(`-`(`/`(`*`(2, `*`(`+`(`-`(`/`(`*`(`/`(1, 2), `*`(`+`(`-`(`*`(`/`(1, 4), `*`(f[alpha, beta], `*`(f[xi, eta], `*`(Physics:-g_[`~alpha`, `~xi`], `*`(Physics:-g_[`~beta`, `~eta`])))...](physics/Physics_560.gif) ![T[`~nu`, `~mu`] = `+`(`-`(`/`(`*`(2, `*`(`+`(`-`(`/`(`*`(`/`(1, 2), `*`(`+`(`-`(`*`(`/`(1, 4), `*`(f[alpha, beta], `*`(f[xi, eta], `*`(Physics:-g_[`~alpha`, `~xi`], `*`(Physics:-g_[`~beta`, `~eta`])))...](physics/Physics_561.gif) |
(123) |
Simplifying the contracted tensor indices we get the expected result
| > |
![T[`~nu`, `~mu`] = `+`(`*`(`/`(1, 4), `*`(Physics:-g_[`~mu`, `~nu`], `*`(`+`(`-`(`*`(2, `*`(`^`(m, 2), `*`(a[beta], `*`(a[`~beta`]))))), `*`(f[beta, xi], `*`(f[`~beta`, `~xi`])))))), `*`(`^`(m, 2), `*`...](physics/Physics_563.gif) |
(124) |
Simplifying spinor, su2, su3 and gauge indices
In previous releases, the Simplify command, for simplifying among other things tensorial expressions, only handled spacetime, space and tetrad indices. In Maple 2020, Simplify also handle spinor, su2, su3 and/or gauge indices taking into account Einstein's sum rule for repeated indices and the possible existence of tensor symmetries. As in previous releases, the tensors are defined as such using Define, and the letters used to represent different kinds of indices are set using Setup, for example: ![]()
Unlike the case of spacetime indices, that can refer to a curved or Minkowski space where the metric is not Euclidean, the metric for spinor, su2, su3 and gauge indices is always Euclidean and represented by KroneckerDelta indexed with indices of the corresponding type. In connection with this development, the dimension of the spaces represented by these indices is automatically set according to:
Examples
| > |
Set spinor, su2 and su3 indices, also an anticommutative prefix to represent a Dirac spinor
| > |
| (125) |
To work with a Dirac spinor using tensor notation, define it first as a tensor
| > |
| (126) |
In view of the anticommutative character of ![]() , the following two expressions are zero
, the following two expressions are zero
| > |
| (127) |
| > |
| (128) |
| > |
| (129) |
| > |
| (130) |
To understand the result above, split the product into two factors, separating the part that contains LeviCivita tensors
| > |
| (131) |
Simplify each part
| > |
| (132) |
From ![]() ,
, ![]()
Related to the ability to simplify and manipulate su2 and su3 indices, the Library:-PerformMatrixOperations command got further developed. For example, consider the fully contracted product of Pauli matrices, both regarding their spacetime index ![]() and their su2matrix indices
and their su2matrix indices ![]()
| > |
| (133) |
| > |
| (134) |
As a more involved case example, consider for instance a Yang-Mills theory with a massless field ![]() where a is a SU2 index (see eq.(12) of sec. 19.4 of ref.[1]). The interaction Lagrangian can be entered as follows:
where a is a SU2 index (see eq.(12) of sec. 19.4 of ref.[1]). The interaction Lagrangian can be entered as follows:
| > |
| (135) |
| > |
| (136) |
Use a compact display to avoid redundant display of functionality
| > |
| (137) |
| > |
| (138) |
The Lagrangian:
| > |
 |
(139) |
The transition probability density at tree-level for a process with two incoming and two outgoing B particles, that is ![]() , where S is the Scattering matrix, is given by
, where S is the Scattering matrix, is given by
| > |
![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][alpha, d](P__1_), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][beta, g](P__2_),...](physics/Physics_623.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][alpha, d](P__1_), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][beta, g](P__2_),...](physics/Physics_624.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][alpha, d](P__1_), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][beta, g](P__2_),...](physics/Physics_625.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][alpha, d](P__1_), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][beta, g](P__2_),...](physics/Physics_629.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][alpha, d](P__1_), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][beta, g](P__2_),...](physics/Physics_630.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][alpha, d](P__1_), `*`(Physics:-FeynmanDiagrams:-PolarizationVector[B][beta, g](P__2_),...](physics/Physics_631.gif) |
(140) |
Due to the use of size simplification, this expression is of computational length ~4000 and has only 4 terms, although each of them nested several times
| > |
| (141) |
| > |
| (142) |
There are several repeated indices of spacetime and su2 kinds that can be simplified though. The command to see information about the indices is Check
| > |
| (143) |
The number of repeated indices in each term is
| > |
| (144) |
Maple 2020 can simplify this expression using Einstein's sum rule for repeated indices and the fact that both the spacetime metric ![]() and the su2 metric
and the su2 metric ![]() are symmetric, applying simplification in size at the end, resulting in an expression with less repeated indices, and where the indices cannot be simplified furthermore
are symmetric, applying simplification in size at the end, resulting in an expression with less repeated indices, and where the indices cannot be simplified furthermore
| > |
![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_647.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_648.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_649.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_650.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_651.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_652.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_653.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_660.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_661.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_662.gif) ![Typesetting:-mprintslash([`+`(`/`(`*`(`*`(`/`(1, 8), `*`(I)), `*`(Dirac(`+`(`-`(P__3[sigma]), `-`(P__4[sigma]), P__1[sigma], P__2[sigma])), `*`(`^`(q, 2), `*`(`+`(`*`(`+`(P__1[`~kappa`], P__2[`~kappa`...](physics/Physics_663.gif) |
(145) |
The repeated indices are now
| > |
| (146) |
So instead of ![]() we now have
we now have
| > |
| (147) |
Psigma definition and algebra and KroneckerDelta as a metric for spinor, su2 and su3 indices
In previous releases, the definition of ![]() (entered as Psigma[mu]), representing a 4-vector whose components are the three Pauli matrices and the identity 2x2 matrix, could not be changed. Likewise,
(entered as Psigma[mu]), representing a 4-vector whose components are the three Pauli matrices and the identity 2x2 matrix, could not be changed. Likewise, ![]() (entered as KroneckerDelta[a,b]) could not be used as a tensor, in order to have the possibility of using it as the standard Kronecker delta symbol, equal to 1 when
(entered as KroneckerDelta[a,b]) could not be used as a tensor, in order to have the possibility of using it as the standard Kronecker delta symbol, equal to 1 when ![]() and equal to 0 otherwise.
and equal to 0 otherwise.
Although that setup is convenient in different situations, it is somewhat rigid: when, for instance, you were to set the signature to (- +++), you'd have ![]() representing the 2x2 identity matrix, not the 1st Pauli matrix; and there was no symbol available to represent the metric in the SU(2), SU(3) or spinor tensor space, where it is actually equal to
representing the 2x2 identity matrix, not the 1st Pauli matrix; and there was no symbol available to represent the metric in the SU(2), SU(3) or spinor tensor space, where it is actually equal to ![]() , a Kronecker delta. The difference between being or not a metric is that, for a metric, due to Einstein's convention of summing over repeated indices
, a Kronecker delta. The difference between being or not a metric is that, for a metric, due to Einstein's convention of summing over repeated indices ![]() , while for the Kronecker delta symbol,
, while for the Kronecker delta symbol, ![]()
To improve the Maple representation capabilities regarding those issues, in Maple 2020:
The Pauli matrices and their representation using Physics:-Psigma
When Physics is loaded, the default metric is of Minkowski type with signature (---+)
| > |
| (148) |
| > |
 |
(149) |
In this framework, the three Pauli matrices, together with the 2x2 identity matrix, form a 4-vector
| > |
| (150) |
Where each ![]() with j from 1 to 3 are the Pauli matrices
with j from 1 to 3 are the Pauli matrices
| > |
 |
(151) |
Note the Pauli matrices are given by the covariant components; there is a change in sign when you consider the components of the contravariant ![]() due to the signature (---+)
due to the signature (---+)
| > |
| (152) |
| > |
 |
(153) |
These matrices form a complete base in the space of 2x2 matrices and satisfy an algebra of commutators and anticommutators that, in Maple 2020, is expressed in 4D tensorial form as
| > |
| (154) |
For example, the commutator rules CP for ![]() are
are
| > |
| (155) |
| > |
 |
(156) |
| > |
 |
(157) |
For the anticommutators
| > |
| (158) |
| > |
 |
(159) |
| > |
 |
(160) |
Note that in the lines above the matricial operations are performed abstractly, with the 2x2 matrices "0" and "1" (identity) omitted. To represent the algebra of the Pauli matrices with those two matrices not omitted, see the approach used in the MaplePrimes post Algebra of the Dirac matrices with an identity matrix on the right-hand side.
Changing the signature, including or not changing also the position of the timelike component, automatically results in corresponding changes in the form of the algebra rules.
Pauli matrices as a 3D tensor
There are two ways to work with the Pauli matrices forming a tensor but in a 3D space. First, provided your spacetime is flat (Minkowski or Euclidean), you can set spaceindices and redo the definition of Psigma. For that it is required that you use the redo option of Define and pass Psigma with spaceindices in the definition. That is particularly useful when you change the signature so that the timelike component is in position 1 and then the 1stcomponent of ![]() is the 2x2 identity matrix, not
is the 2x2 identity matrix, not ![]() . For example
. For example
| > |
| (161) |
Due to having the timelike component in position one, ![]() is the identity matrix, and the 1st Pauli matrix is given by
is the identity matrix, and the 1st Pauli matrix is given by ![]()
| > |
 |
(162) |
| > |
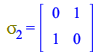 |
(163) |
Set spaceindices and redo the definition of Psigma with a space index
| > |
| (164) |
| > |
| (165) |
Now you can work with the signature (+ ---) and have ![]() be
be ![]() , the 1st Pauli matrix
, the 1st Pauli matrix
| > |
 |
(166) |
Accordingly, the algebra is expressed in terms of 3D tensors (the usual way), using the 3D metric ![]() instead of the 4D metric
instead of the 4D metric ![]()
| > |
| (167) |
where
| > |
| (168) |
| > |
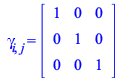 |
(169) |
| > |
 |
(170) |
Hence,
| > |
 |
(171) |
Another way to work with the Pauli matrices forming a tensor in a 3D space, avoiding the details related to the value of the signature, the position of the timelike component, and whether the spacetime set is flat or curved, you can redefine Psigma as a 3D tensor in an abstract SU(2) space, that is, an Euclidean 3-dimensional space, where the metric is represented by the KroneckerDelta. For example
| > |
| (172) |
| > |
| (173) |
| > |
| (174) |
| > |
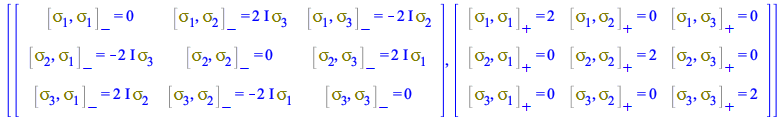 |
(175) |
| > |
 |
(176) |
KroneckerDelta as a metric for su2, su2matrix, su3, su3matrix, spinor and gauge indices
In Maple 2020, the KroneckerDelta command can be used with two different purposes:
This has the representational advantage of addressing both computational requirements and in the same way they are addressed in textbooks.
| > |
| (177) |
KroneckerDelta behaves like a metric (![]() ) only when it is indexed with indices of spinor, su2, su2matrix, su3, su3matrix, or gauge indices.
) only when it is indexed with indices of spinor, su2, su2matrix, su3, su3matrix, or gauge indices.
| > |
| (178) |
Indexing with space or spacetime indices, still results in the KroneckerDelta symbols, not the metric (the space and spacetime metrics are respectively represented by the gamma_ and g_ commands)
| > |
| (179) |
For all the other spaces for which you set corresponding indices, KroneckerDelta behaves as a metric. The su2indices run from 1 to 3, the dimension of SU(2). The related matrices are the Pauli matrices.
| > |
| (180) |
The dimension of spinorindices is the one of the Dirac matrices, equal to the spacetime dimension only in a 4-dimensional spacetime
| > |
| (181) |
The su3indices run from 1 to 8, the dimension of SU(3); the related matrices are the Gell-Mann matrices, represented in Maple by ![]() .
.
| > |
| (182) |
You can still use gaugeindices of an some generic dimension (not set), and use KroneckerDelta to represent the metric in that dimension. In that case, the trace returns uncomputed and, as in the other cases, you can use this KroneckerDelta metric to simplify tensorial expressions using these indices
| > |
| (183) |
The trace remains uncomputed, the dimension of gaugeindices is generic, not set
| > |
| (184) |
You can simplify tensorial expressions involving these indices. Define a tensor in this gauge space
| > |
| (185) |
| > |
| (186) |
| > |
| (187) |
| > |
| (188) |
| > |
| (189) |
A number of minor changes happened in several places of the Physics library for Maple 2020, improving performance and the computational experience.
| > |
| (190) |
| > |
| (191) |
Define now a tensor that, by construction is antisymmetric, but do not tell the system about that (anti)symmetry property
| > |
| (192) |
| > |
| (193) |
At run time, the symmetry property of this definition got noticed and tracked, so that it can be retrieved by all any command that takes symmetries into account
| > |
| (194) |
| > |
| (195) |
| > |
| (196) |
| > |
| (197) |
| > |
| (198) |
The ![]() are now recognized as the components of a Dirac Spinor using the new
are now recognized as the components of a Dirac Spinor using the new ![]() type: any anticommutative object indexed with spinorindices is considered a Dirac spinor
type: any anticommutative object indexed with spinorindices is considered a Dirac spinor
| > |
| (199) |
Accordingly, the Einstein sum rule for repeated indices applies
| > |
| (200) |
| > |
 |
(201) |
Improvements for functional differentiation regarding generic non-commutative tensor fields
| > |
 |
(202) |
Define a tensor with spacetime and spinor indices
| > |
| (203) |
Note the occurrence of both the spacetime metric ![]() ≡
≡![]() and the spinor metric
and the spinor metric ![]() represented by KroneckerDelta:
represented by KroneckerDelta:
| > |
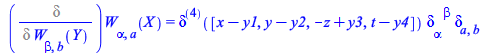 |
(204) |
Likewise, the Physics diff command can now perform the related differentiation
| > |
| (205) |
| > |
| (206) |
| > |
| (207) |
| > |
| (208) |
The new option disregardfreeindicesinsubstitutionequation of SubstituteTensor: before Maple 2020, the following interrupts with an appropriate error message
| > |
| Error, (in Physics:-SubstituteTensor) free indices in both sides of the equation are different: found {i, j, mu} on the left-hand side and {} on the right-hand side |Physics/src/Check.mm:113| |
However, substitutions where the free indices in both sides of a substitution equation are different could be intentional; in those cases you can use the new option
| > |
| (209) |
| > |
| (210) |
| > |
| (211) |
| > |
| (212) |
Compare the output of these two uses of TensorArray
| > |
 |
(213) |
When what is desired is to have each component of the Array equal to 0, to form a system of equations, use the new option output = setofequations
| > |
| (214) |
The ![]() are now recognized as the components of a Dirac Spinor using the new
are now recognized as the components of a Dirac Spinor using the new ![]() type: any anticommutative object indexed with spinorindices is considered a Dirac spinor
type: any anticommutative object indexed with spinorindices is considered a Dirac spinor
| > |
| (215) |
Given any 2-rank tensor (representable by a matrix), the design in the Physics package is that its determinant is computed when you index the tensor with the keyword determinant. For example, set the metric g_ to be arbitrary
| > |
 |
(216) |
| > |
| (217) |
Depending on the formulation, however, to perform algebraic manipulations what is required is a representation of the determinant, not its computed value. For that purpose use the inert form
| > |
| (218) |
that you can activate when desired using value.
| > |
| (219) |